
Stay informed with our latest tips, guides, and updates via email.
Join our mailing list for expert tips, practical how-tos, and the latest industry trends—no fluff, just value. Stay sharp and ahead in tech.
Choosing the right database is one of the most important decisions in any software project. With a wide range of options available—each offering distinct architectures, features, and performance trade-offs—the selection process can feel overwhelming. But by taking a structured and informed approach, you can confidently choose the right solution for your specific needs.
Define Your Project Requirements
Every project has unique data needs. Before diving into specific database options, it’s essential to understand:
- What type of data are you storing—structured, semi-structured, or unstructured?
- How large is the data volume, and how fast is it expected to grow?
- What kind of operations will you run—are they mostly reads, writes, or complex queries?
- Do you prioritize consistency, availability, or partition tolerance?
- Will the system handle real-time data or operate in batches?
A clear definition of your requirements will help narrow down your options early.
Understand the Different Types of Databases
There are three primary categories of databases:
Relational Databases (SQL)
These use structured schemas and store data in tables. They’re ideal for applications requiring complex queries, strong consistency, and transactional integrity. Examples include MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and SQL Server.
Non-Relational Databases (NoSQL)
These databases store data in more flexible formats such as documents, key-value pairs, or graphs. They’re great for scalability and handling unstructured or rapidly changing data. Examples include MongoDB, Redis, Cassandra, and Neo4j.
Hybrid Databases
Some modern databases offer hybrid models that blend the features of SQL and NoSQL databases, giving developers the flexibility to work with different data types and access patterns in one platform.
Compare Popular Database Solutions

Once you understand the type of database that suits your project, you can evaluate individual options based on performance, community support, ease of use, and ecosystem compatibility.
Here are a few widely used options:
- PostgreSQL – An open-source relational database known for its powerful SQL engine, extensibility, and strong data integrity features.
- MySQL – A lightweight and easy-to-use relational database popular in web development.
- MongoDB – A document-based NoSQL database great for flexible schemas and JSON-like data storage.
- Redis – A high-speed in-memory key-value store often used for caching and real-time analytics.
- Neo4j – A leading graph database ideal for storing and querying complex relationships.
- Cassandra – A distributed database built for handling large-scale data across many servers with high availability.
- DynamoDB – AWS’s fully managed NoSQL solution with seamless scalability and low-latency performance.
Consider SaaS-Based Database Platforms
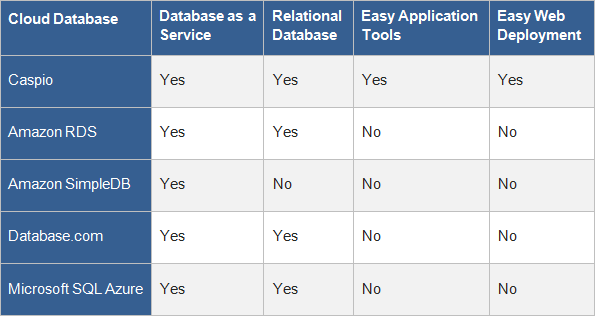
If you’re looking to minimize infrastructure management and operational overhead, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) database platforms can be a great choice. Here are some popular options:
Firebase
A Google-backed platform offering backend services for web and mobile apps. It includes a real-time database and Cloud Firestore for flexible document storage and real-time syncing, along with hosting, authentication, and analytics support.
MongoDB Atlas
A fully managed cloud version of MongoDB that supports easy deployment across AWS, Azure, and GCP. It offers built-in monitoring, backup, security features, and performance tuning tools.
Amazon RDS
A managed relational database service from AWS that supports MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server, and MariaDB. RDS handles tasks like provisioning, backups, patching, and failover, letting you focus on your application.
Test Before You Commit
Even with strong contenders, hands-on testing is essential. Simulate your production environment to evaluate:
- Performance under expected workloads
- Read and write latency
- Query handling and indexing
- Integration with your technology stack
- Backup and recovery processes
Use load testing tools and monitoring dashboards to gain deeper insight into how each database behaves under pressure.
Make a Confident Decision
After testing, compare your findings against your initial requirements. Consider not only technical performance but also long-term factors such as:
- Licensing and operating costs
- Community and support availability
- Learning curve and developer productivity
- Vendor lock-in and cloud compatibility
Keep in mind that your project may benefit from using multiple databases for different tasks—a practice known as polyglot persistence.

Stay informed with our latest tips, guides, and updates via email.
Join our mailing list for expert tips, practical how-tos, and the latest industry trends—no fluff, just value. Stay sharp and ahead in tech.
